Publications
2024
-
 Multi-Modal Self-Supervised Learning for Surgical Feedback Effectiveness AssessmentArushi Gupta*, Rafal D. Kocielnik*, Jiayun Wang, Firdavs Nasriddinov, Cherine Yang, Elyssa Wong, Anima Anandkumar, and Andrew J. HungMachine Learning for Health (ML4H) Symposium, 2024
Multi-Modal Self-Supervised Learning for Surgical Feedback Effectiveness AssessmentArushi Gupta*, Rafal D. Kocielnik*, Jiayun Wang, Firdavs Nasriddinov, Cherine Yang, Elyssa Wong, Anima Anandkumar, and Andrew J. HungMachine Learning for Health (ML4H) Symposium, 2024The paper won the best paper award at 2024 Machine Learning for Health Conference.
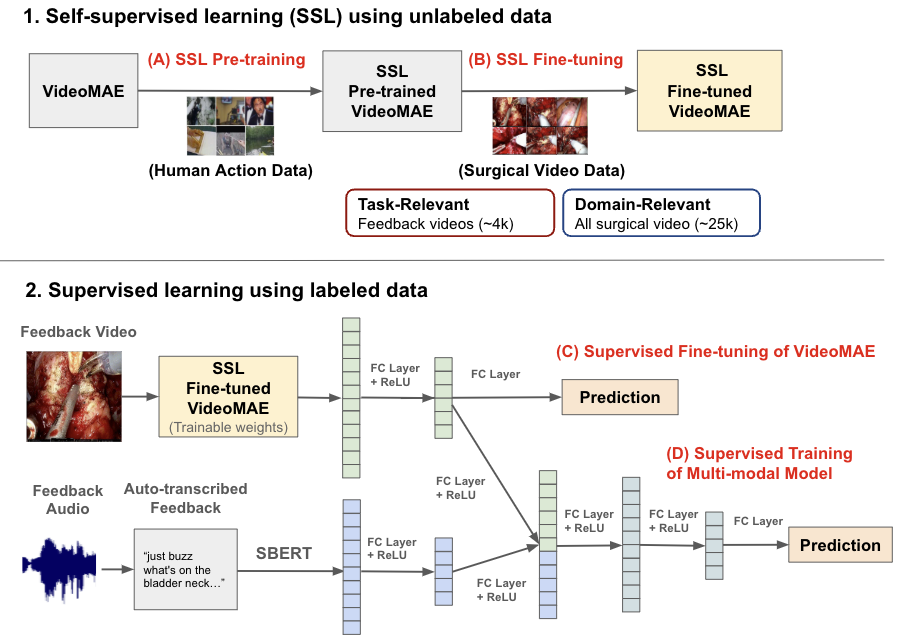
During surgical training, real-time feedback from trainers to trainees is important for preventing errors and enhancing long-term skill acquisition. Accurately predicting the effectiveness of this feedback, specifically whether it leads to a change in trainee behavior, is crucial for developing methods for improving surgical training and education. However, relying on human annotations to assess feedback effectiveness is laborious and prone to biases, underscoring the need for an automated, scalable, and objective method. Creating such an automated system poses challenges, as it requires an understanding of both the verbal feedback delivered by the trainer and the visual context of the real-time surgical scene. To address this, we propose a method that integrates information from transcribed verbal feedback and corresponding surgical video to predict feedback effectiveness. Our findings show that both transcribed feedback and surgical video are individually predictive of trainee behavior changes, and their combination achieves an AUROC of 0.70+/-0.02, improving prediction accuracy by up to 6.6%. Additionally, we introduce self-supervised fine-tuning as a strategy for enhancing surgical video representation learning, which is scalable and further enhances prediction performance. Our results demonstrate the potential of multi-modal learning to advance the automated assessment of surgical feedback.
-
 Automating Feedback Analysis in Surgical Training: Detection, Categorization, and AssessmentFirdavs Nasriddinov*, Rafal D. Kocielnik*, Arushi Gupta, Cherine Yang, Elyssa Wong, Anima Anandkumar, and Andrew HungMachine Learning for Health (ML4H) Symposium, 2024
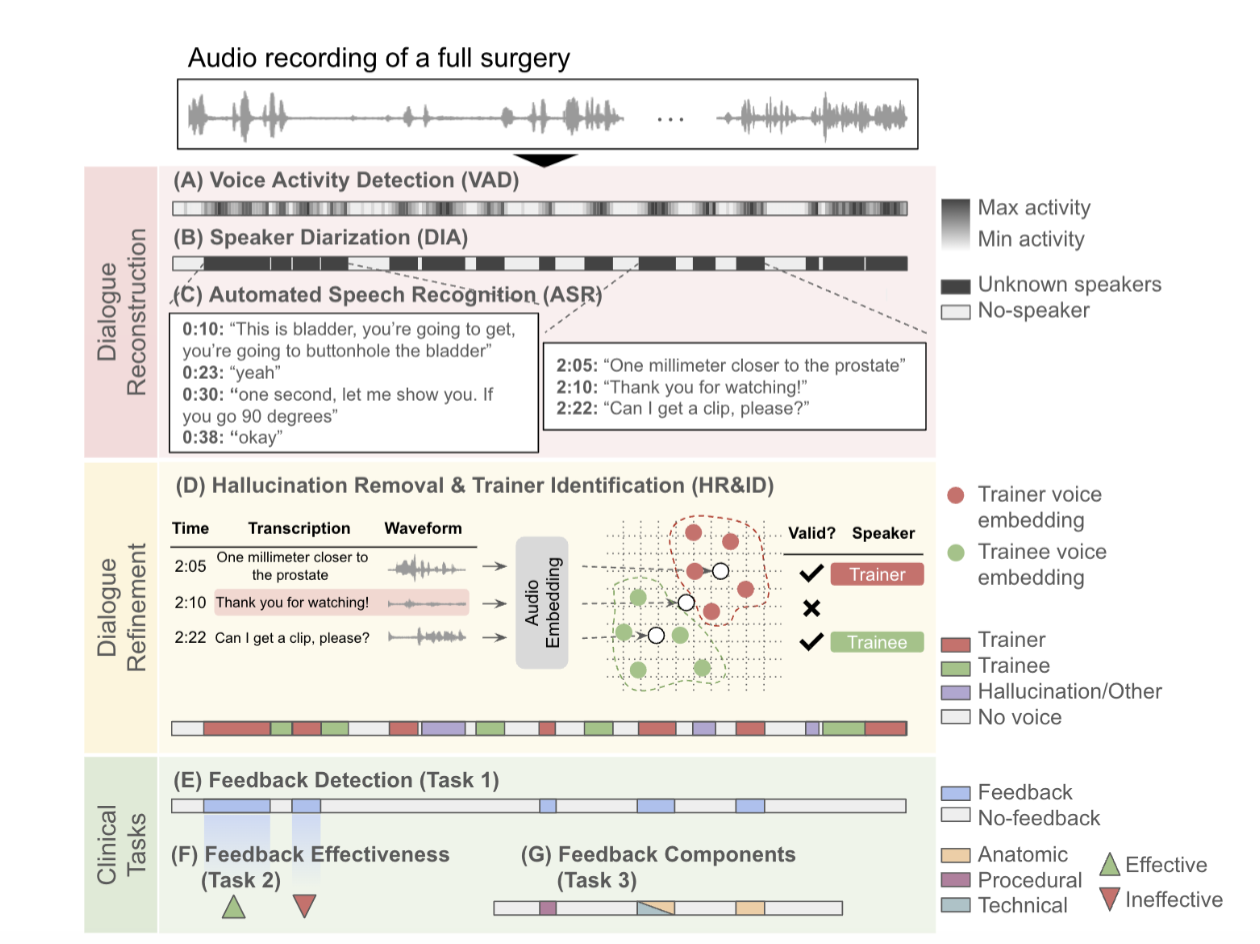
Automating Feedback Analysis in Surgical Training: Detection, Categorization, and AssessmentFirdavs Nasriddinov*, Rafal D. Kocielnik*, Arushi Gupta, Cherine Yang, Elyssa Wong, Anima Anandkumar, and Andrew HungMachine Learning for Health (ML4H) Symposium, 2024This work introduces the first framework for reconstructing surgical dialogue from unstructured real-world recordings, which is crucial for characterizing teaching tasks. In surgical training, the formative verbal feedback that trainers provide to trainees during live surgeries is crucial for ensuring safety, correcting behavior immediately, and facilitating long-term skill acquisition. However, analyzing and quantifying this feedback is challenging due to its unstructured and specialized nature. Automated systems are essential to manage these complexities at scale, allowing for the creation of structured datasets that enhance feedback analysis and improve surgical education. Our framework integrates voice activity detection, speaker diarization, and automated speech recognition, with a novel enhancement that 1) removes hallucinations (non-existent utterances generated during speech recognition fueled by noise in the operating room) and 2) separates speech from trainers and trainees using few-shot voice samples. These aspects are vital for reconstructing accurate surgical dialogues and understanding the roles of operating room participants. Using data from 33 real-world surgeries, we demonstrated the system’s capability to reconstruct surgical teaching dialogues and detect feedback instances effectively (F1 score of 0.79+/-0.07. Moreover, our hallucination removal step improves feedback detection performance by 14%. Evaluation on downstream clinically relevant tasks of predicting Behavioral Adjustment of trainees and classifying Technical feedback, showed performances comparable to manual annotations with F1 scores of 0.82+/-0.03 and 0.81+/-0.03 respectively. These results highlight the effectiveness of our framework in supporting clinically relevant tasks and improving over manual methods.
2023
-
 Greedy Learning for Memory-Efficient Self-Supervised MRI ReconstructionArushi Gupta, Batu M. Ozturkler, Arda Sahiner, Tolga Ergen, Arjun D. Desai, Shreyas Vasanawala, John M. Pauly, Morteza Mardani, and Mert PilanciInternational Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) Annual Meeting, 2023
Greedy Learning for Memory-Efficient Self-Supervised MRI ReconstructionArushi Gupta, Batu M. Ozturkler, Arda Sahiner, Tolga Ergen, Arjun D. Desai, Shreyas Vasanawala, John M. Pauly, Morteza Mardani, and Mert PilanciInternational Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) Annual Meeting, 2023Deep learning (DL) has recently shown state-of-the-art performance for accelerated MRI reconstruction. However, supervised learning requires fully-sampled training data, and training these networks with end-to-end backpropagation requires significant memory for high-dimensional imaging. These challenges limit the use of DL in high-dimensional settings where access to fully-sampled data is unavailable. Here, we propose self-supervised greedy learning for memory-efficient MRI reconstruction without fully-sampled data. The method divides the end-to-end network into smaller network modules and independently calculates a self-supervised loss for each subnetwork. The proposed method generalizes as well as end-to-end learning without fully-sampled data with at least 7x less memory usage.